Openshift local installation guide
Openshift Local is the free edition for developers of Red Hat’s container platform. It provides a single-node Openshift cluster for testing.
In this post I explain how to install and manage the CodeReady Containers for OKD virtual machine that contains an Openshift local version that doesn’t require a Red Hat account.
The commands were run in Windows 11 Pro with a computer with an Intel i5-13600KF processor, and 32 GB of RAM.
Most of the commands can run on Linux with no modifications.
Minimum requirements
- Hardware virtualization
- A 64-bit x86_64 CPU with 4 cores or more
- At least 9GB of RAM free
- 35 GB of free disk space
- Windows or Linux
Prerequisites
You must install the crc command for installing and managing Openshift Local.
Download and run the crc installer from developers.redhat.com - crc installer
In Windows, the installer will enable Hyper-V on your machine, but crc also requires the Hyper-V Poweshell module. To ensure the module is installed, open an administrator terminal, run Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V-Management-PowerShell, and restart your pc.
Installation
Now let’s download and install the CodeReady Containers for OKD VM.
Open a terminal with no root or admin privileges and follow these steps:
-
By default crc installs an Openshift local version that requires to be linked with a Red Hat account. Run the command
crc config set preset okdto switch to CodeReady Containers for OKD.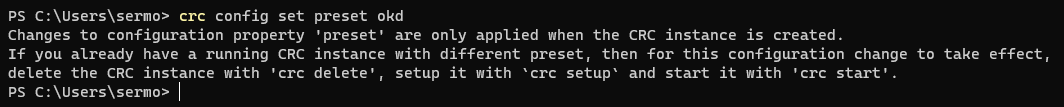
-
Next, run
crc setupto download and install the virtual machine.
IMPORTANT: The process will open a terminal of crc daemon that acts as a middleware between crc and the Openshift Local cluster. Don’t close the window because it will stop the daemon too. In case you closed it, run
crc setupto start it again.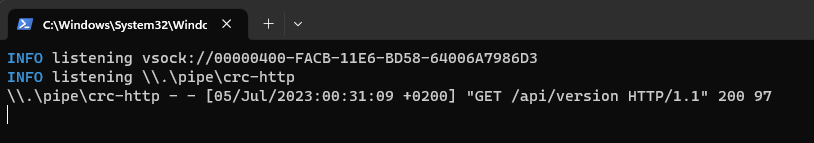
-
Run
crc startto start the virtual machine. The first boot will take 5-10 minutes to get the Openshift Local cluster ready.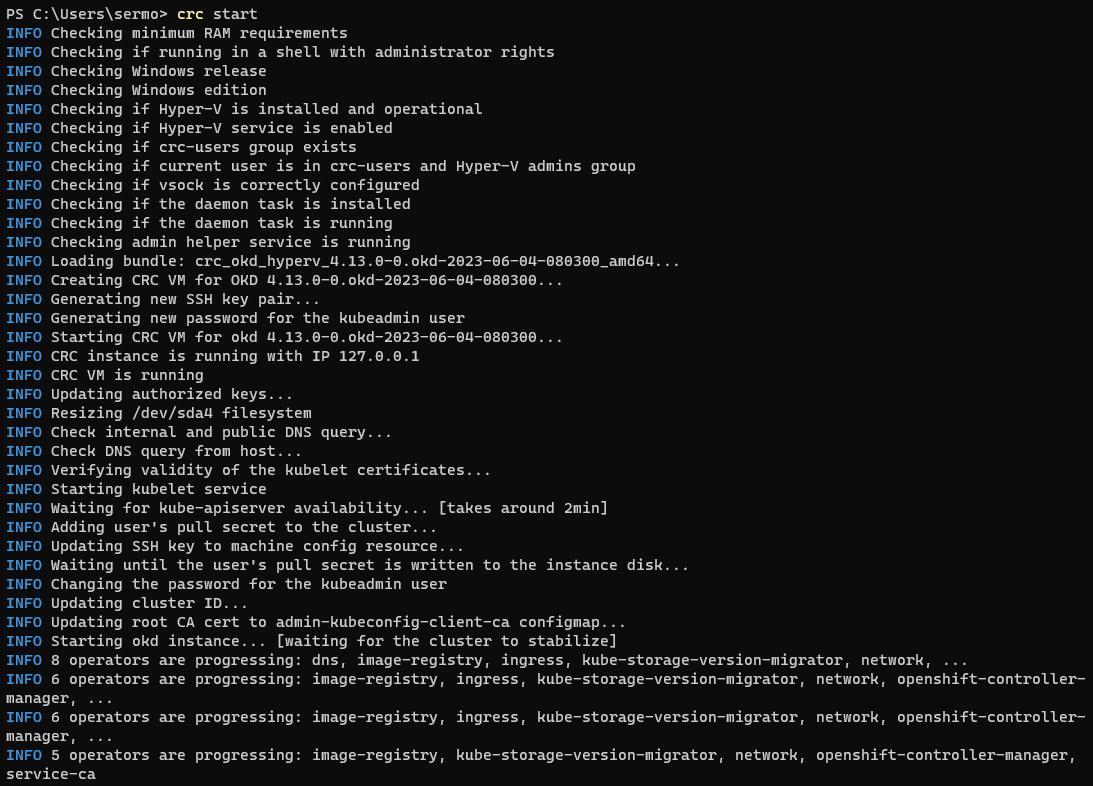
Throubleshooting
If you saw the message “Error starting machine: Error in driver during machine start: exit status 1” it means there’s not enough free RAM to start the VM. To fix it, close apps and try again. -
The connection parameters and credentials of Openshift local cluster will be shown at the end of the start log.
In case you didn’t see it, run againcrc startto show it again.
-
Open the web console and log in with the user kubeadmin or developer
Your browser may show a security alert the first time you open the web console. Don’t worry: This is because it has a self-signed certificate. Just click on continue and enter the credentials.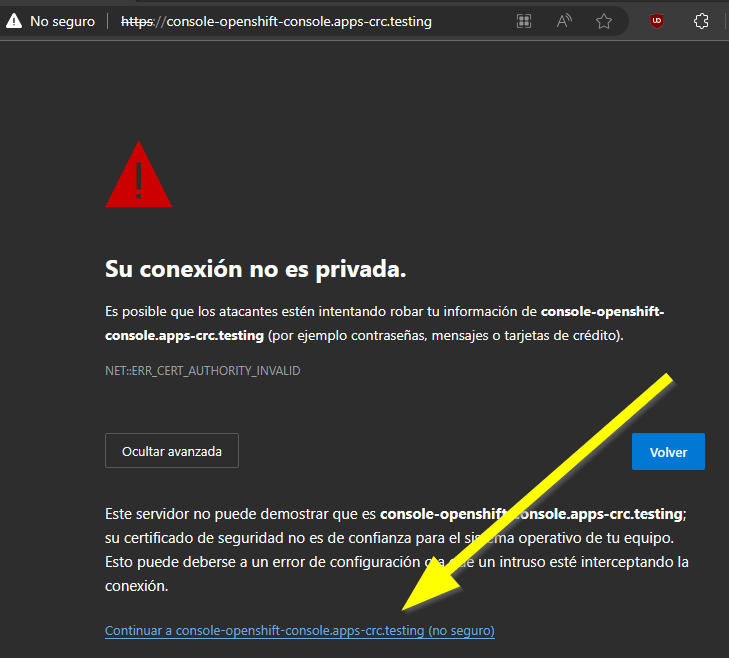
-
Finally, you may install the command oc to manage the Openshift Cluster from terminal by running
crc oc-envand following the intructions.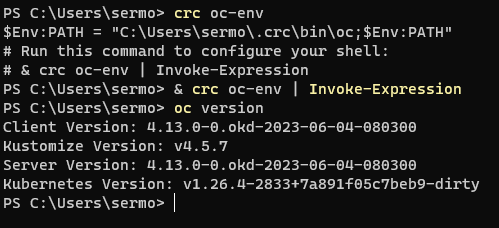
To stop the Openshift local cluster run crc stop
Improving the performance of CodeReady Containers for OKD VM in Windows
In Windows I recommend to review and change Hyper-V settings of the CodeReady Containers for OKD VM because by default it won’t use all the performance of your computer.
- Open Hyper-V manager and go to the settings of the virtual machine named crc.
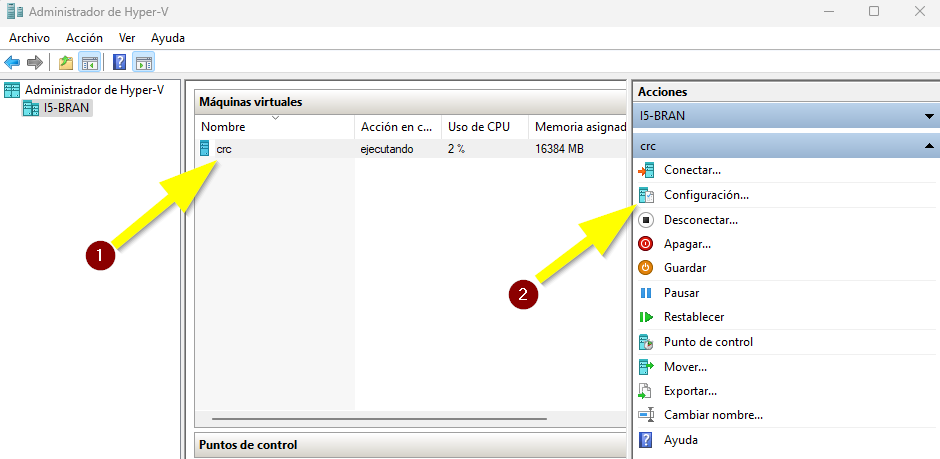
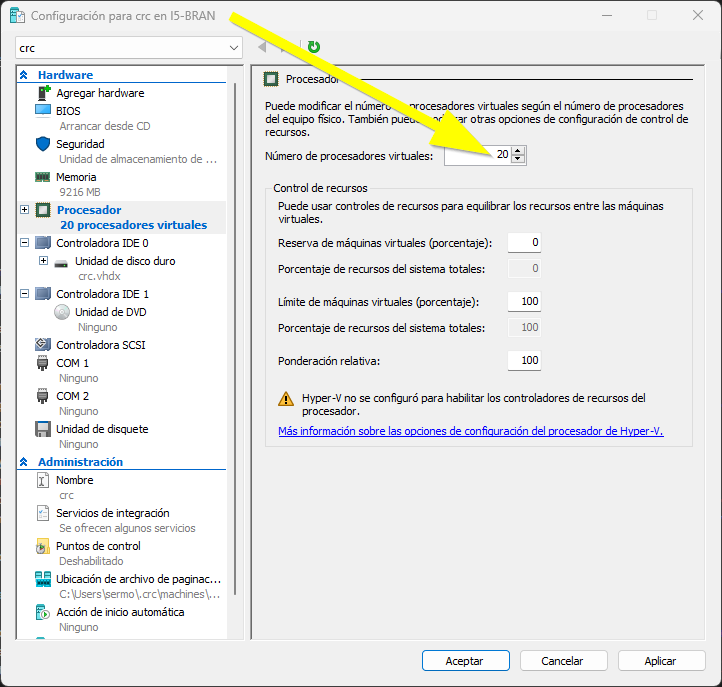
- Open the processor tab. By default the VM has 4 processors. I recommend increasing the value up to the number of logical processors of your physical computer to get the best performance.
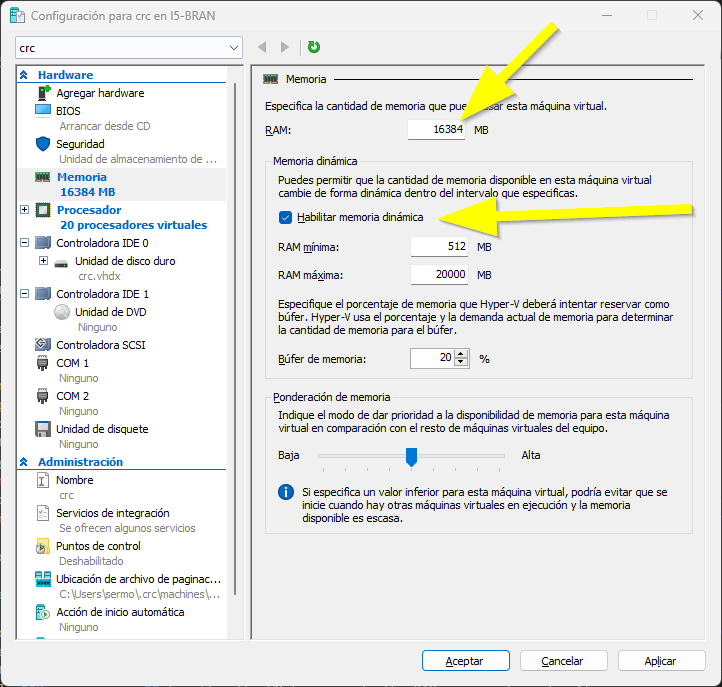
- Next open the memory tab and enable Dynamic memory to allow the VM to use only the RAM memory it needs. Also, you can increase the memory to be able to run more pods at once.
Upgrade Openshift local version
To upgrade the version of the Openshift Local cluster login to the web console as kubeadmin and click in the Update cluster link of the details section. 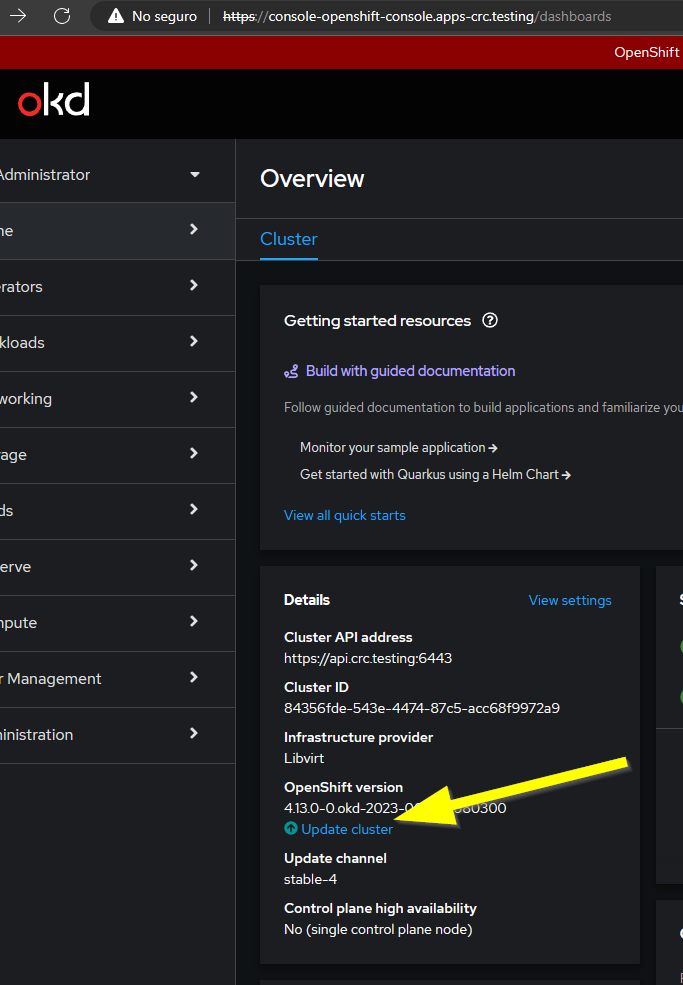
Delete Openshift local cluster
Simply run crc delete